skeleton of the back
.lumbar vertebrae differ from thoracic vertebrae in the fol-
lowing ways (Fig. 1.05): lumbar vertebrae have larger bodis,
broad spinous process that project posteriorly, and they do not
have articular facets for ribs. On a skeleton, observe the lumbar
vertebrae and notice that their spins do not overlap like the
spines of thoracic vertebrae. [6 Z89; N 148; R 1%; C 426]
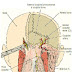
The sacrum is formed by five fused vertebrae and it does not
have identifiable spins or transverse process. On the dorsal
surface of the sacrum, identify (Fig. 1.06): [G Z93; N 150; ll ‘I87;
C418]
° Median sacral crest
° Posterior (dorsal) sacral foramina
' Sacral hiatus
The ooecyx is a small triangular bone formed by four rudi-
mentary coocygeal vertebrae that are fused together (Fig. 1.06).
SKIN AND SUPERFICIAL FASCIA
Before you dissect . . .
The order of disection will be as follows: the skin will be
removed from the back, posterior surface of the neck, and pos-
terior surface of the proximal upper limb. Posterior cutaneous
nervs will be studied. The superficial fscia will then be
removed









0 التعليقات:
إرسال تعليق